Acoustic scene classification using deep cnn with fine-resolution feature
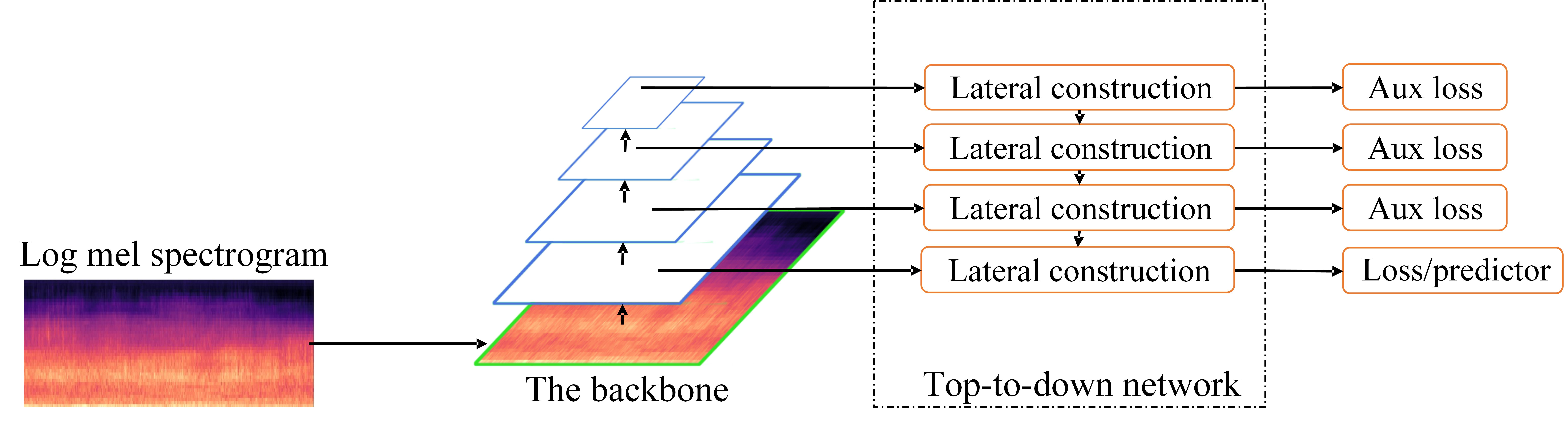
What is the rule of thumb to design an audio network from scratch? We came up with a new concept named time-frequency feature resolution to devise a model using priori knowledge in audio durations. Under the guidance of time-frequency feature resolution, we propose FRCNN to classify acoustic scenes in recordings.
See more details in the paper If you find this paper is helpful, please cite this paper.
@article{ZHANG2020113067,
title = {Acoustic scene classification using deep CNN with fine-resolution feature},
journal = {Expert Systems with Applications},
volume = {143},
pages = {113067},
year = {2020},
issn = {0957-4174},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.113067},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0957417419307845},
author = {Tao Zhang and Jinhua Liang and Biyun Ding},
keywords = {Acoustic scene classification, Convolutional neural network, Lateral construction, Depth-wise separable convolution, Fine-resolution convolutional neural network},
abstract = {Convolutional neural networks with spectrogram feature representation for acoustic scene classification are attracting more and more attentions due to its favorable performance. However, most of the existing methods are still restricted to the tradeoff between the minimum coverage area across time-frequency feature representation, i.e. time-frequency feature resolution, and the depth of CNN models. Thus, it is unfeasible to improve the performance by simply deepening networks. In this paper, fine-resolution convolutional neural network (FRCNN) is proposed to embrace the progress in very deep architecture, feature fusion and convolutional operation. Specifically, lateral construction is applied to generate a fine-resolution feature map with semantic information, and depth-wise separable convolution is utilized to reduce the number of trainable parameters. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed FRCNN exhibits high performance on several metrics, with low computational complexity.}
}
